
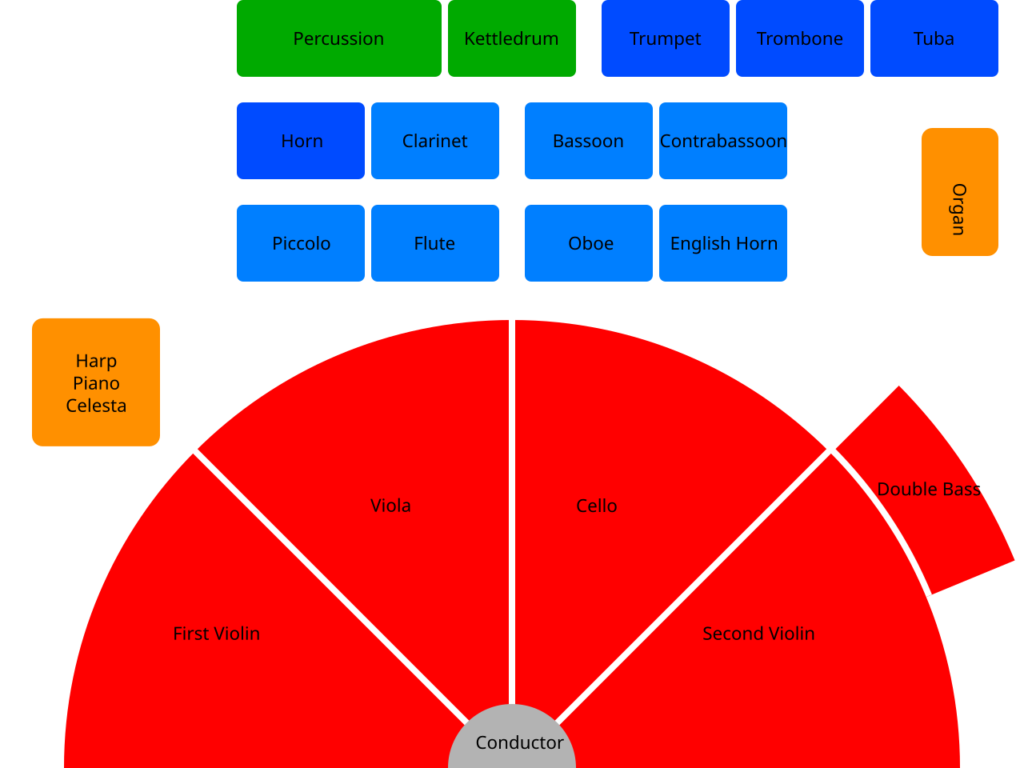
The Orchestral instruments are a diverse group of musical instruments that are typically used in orchestras, which are large ensembles that combine various instrumental sections. These instruments can be categorized into four main families: strings, woodwinds, brass, and percussion. Each section contributes its unique sound and character to orchestral music.
String Instruments
The string family is often considered the heart of the orchestra. Instruments in this category include:
- Violin: The highest-pitched string instrument, known for its agility and expressiveness.
- Viola: Slightly larger than the violin, the viola has a deeper, richer sound and plays inner harmonies.
- Cello: Known for its warm, resonant tone, the cello plays the bass lines and can also perform melodic solos.
- Double Bass: The largest string instrument, providing the foundation of harmony with its deep, powerful sound.
- Harp: A unique string instrument played by plucking the strings, adding a distinctive texture to orchestral music.
Woodwind Instruments
Woodwind instruments are characterized by their use of reeds or air columns to produce sound. They include:
- Flute: A soprano instrument, the flute produces a bright, airy sound and is often featured in melodic passages.
- Oboe: Known for its penetrating and expressive tone, the oboe plays both melodic and harmonic roles in the orchestra.
- Clarinet: A versatile instrument with a rich tone, the clarinet can play a wide range of dynamics and styles.
- Bassoon: The bassoon has a deep, reedy sound and often plays lower harmonies, as well as humorous or characterful passages.
Brass Instruments
Brass instruments are made of metal and produce sound through the vibration of the player’s lips. Common brass instruments include:
- Trumpet: The highest-pitched brass instrument, known for its bright and powerful sound.
- French Horn: With a rich and warm tone, the French horn is known for its versatility and blending capabilities.
- Trombone: Recognizable by its slide mechanism, the trombone can produce a wide range of pitches and is often used for dramatic effects.
- Tuba: The largest brass instrument, the tuba provides the bass foundation of the brass section with its deep, resonant sound.
Percussion Instruments
Percussion instruments produce sound by being struck, shaken, or scraped. This category includes:
- Timpani: Also known as kettle drums, timpani are tuned percussion instruments that provide rhythm and depth to orchestral music.
- Snare Drum: A key component of the percussion section, the snare drum adds sharp rhythmic accents.
- Cymbals: Often used for dramatic crashes or accents, cymbals add brilliance and texture to orchestral pieces.
- Marimba/Percussion Instruments: These include a variety of mallet instruments and auxiliary percussion, contributing unique colors and rhythms.
Each of these instrument plays a vital role in orchestral performances, whether it be through melody, harmony, or rhythm, contributing to the overall musical experience. The collaboration and interplay between these instruments allow for a wide range of expressions and styles, making orchestral music a dynamic and captivating art form.

Download, listen, create with the available samples: